Turbidity curtains are tools used in water management. They help control silt and sediment water clarity and protect the environment. Our curtains are made of durable, UV-resistant PVC fabric and include flotation devices on the top and weighted ballast systems on the bottom. They float on the water’s surface and create a barrier.
When construction or dredging operations happens, dirt and debris can cloud the water. Turbidity curtains stop this from spreading. They trap sediment and keep the water clear. This helps fish and other wildlife stay safe.
To use turbidity curtains, workers place them around the work area. This ensures they block sediment effectively.
Turbidity curtains are important for keeping water clean. They help maintain healthy ecosystems. By using them, we can protect our natural resources.
In construction, dredging, and marine projects, managing water pollution is a critical concern. One of the best tools for controlling sediment is the turbidity curtain. It helps stop sediment from spreading into nearby water bodies. But what exactly is a turbidity curtain, and how does it work? Let’s dive in to explore this essential piece of environmental protection equipment.
What Is a Turbidity Curtain?
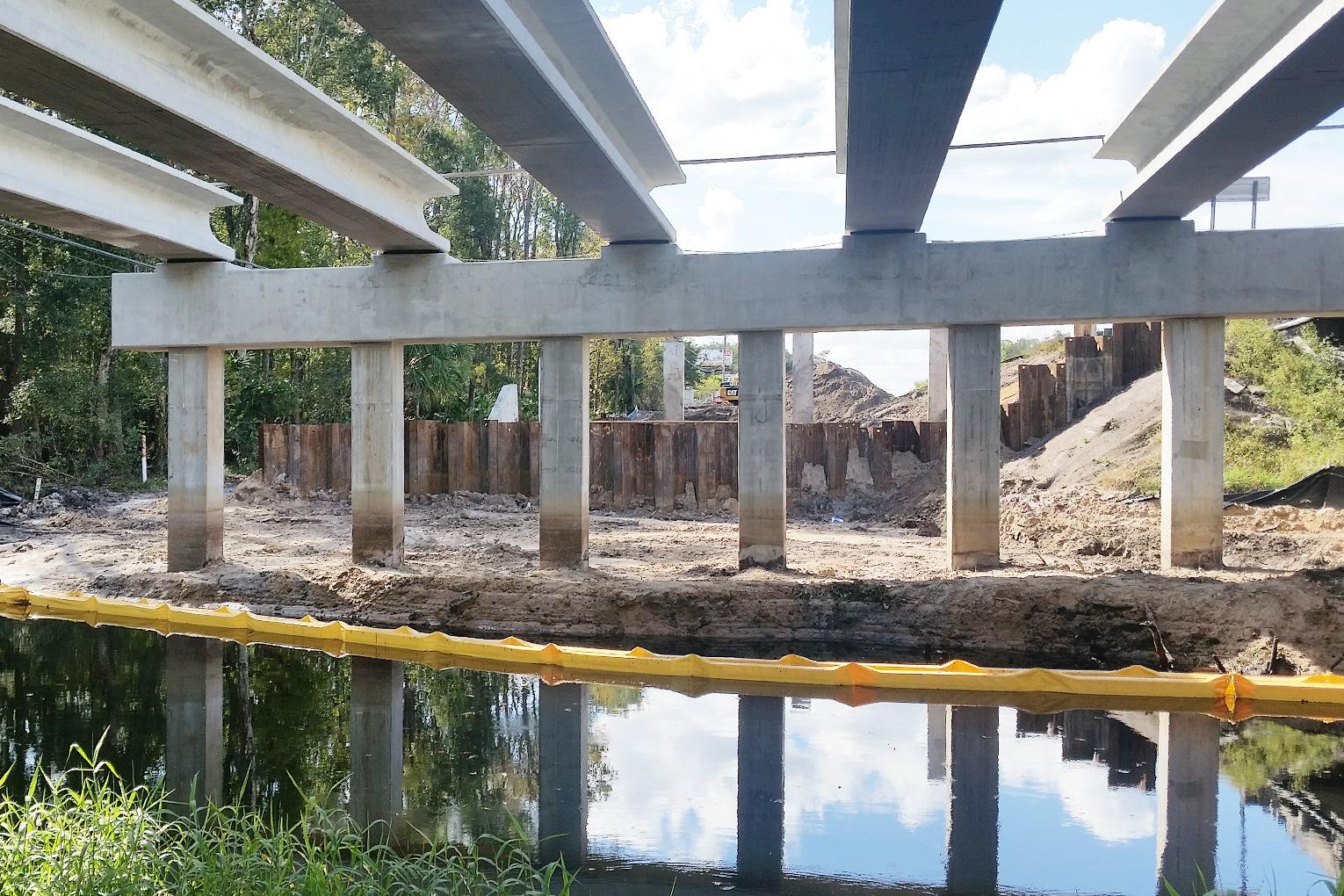
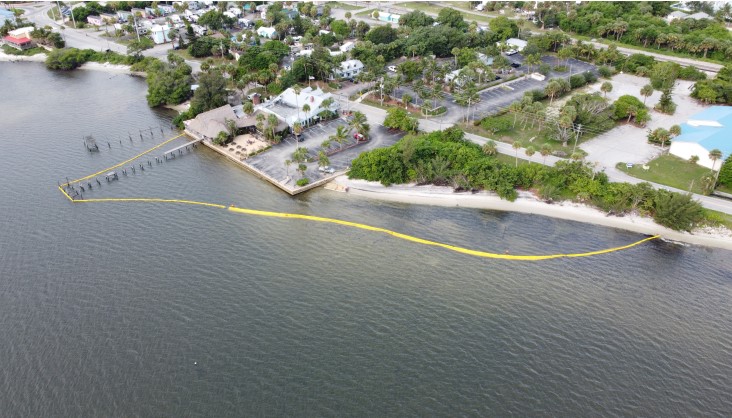
A turbidity curtain, also called a silt barrier or silt curtain, is a floating barrier. It helps control the spread of suspended sediments in water. These curtains are used in both fresh and saltwater environments during construction or dredging activities to prevent sediment from drifting beyond the worksite and impacting marine life or water quality.
Turbidity curtains are typically made from durable, UV-resistant PVC fabric and include flotation devices on the top and weighted ballast systems on the bottom. This design ensures the curtain remains upright in the water, forming an effective barrier from the surface to a specified depth.
Also Known As:
Turbidity curtains are also referred to by several other names, including:
-
Silt Curtains
-
Silt Barriers
-
Floating Silt Barriers
-
Sediment Curtains
-
Turbidity Barriers
-
Floating Turbidity Barriers
How Turbidity Curtains Work
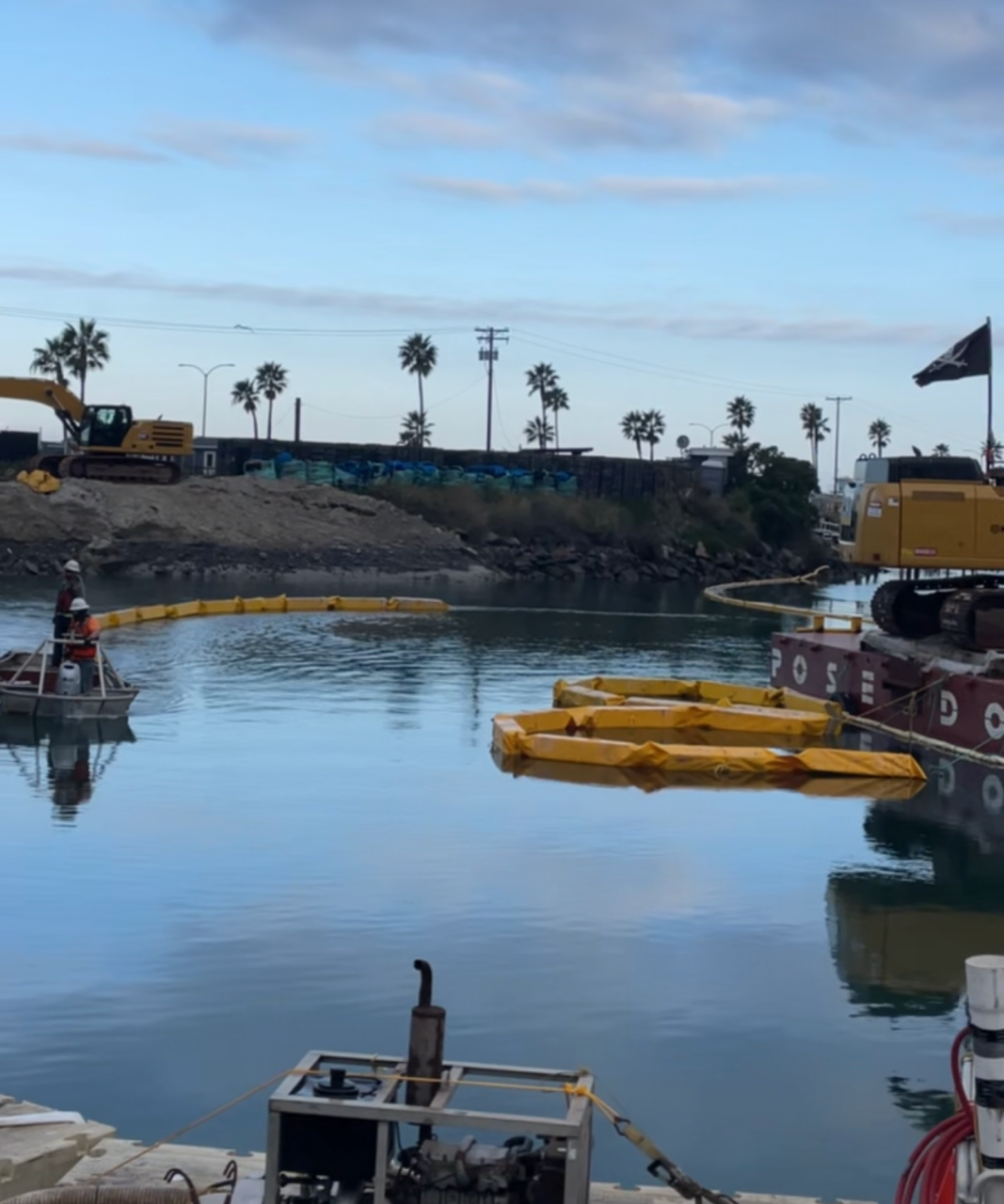
Turbidity curtains function by creating a physical barrier that traps sediment within a designated area. Here’s how they operate in various conditions:
- Deployment
The first step is to determine anchoring points to secure the curtain in place. Proper anchoring ensures the curtain remains stable and doesn’t drift away due to currents or wave height. Depending on the conditions of the body of water, the curtain may be anchored to the seabed or left to float with surface anchors.
- Containment
As construction or dredging stirs up sediment, the curtain prevents particles from spreading into the surrounding water. The floating top ensures the curtain remains on the water’s surface, while the weighted bottom keeps it in place vertically.
- Settling
Sediment particles settle to the bottom over time due to gravity. The curtain helps speed up this natural process by limiting water flow and keeping sediment contained within the work zone.
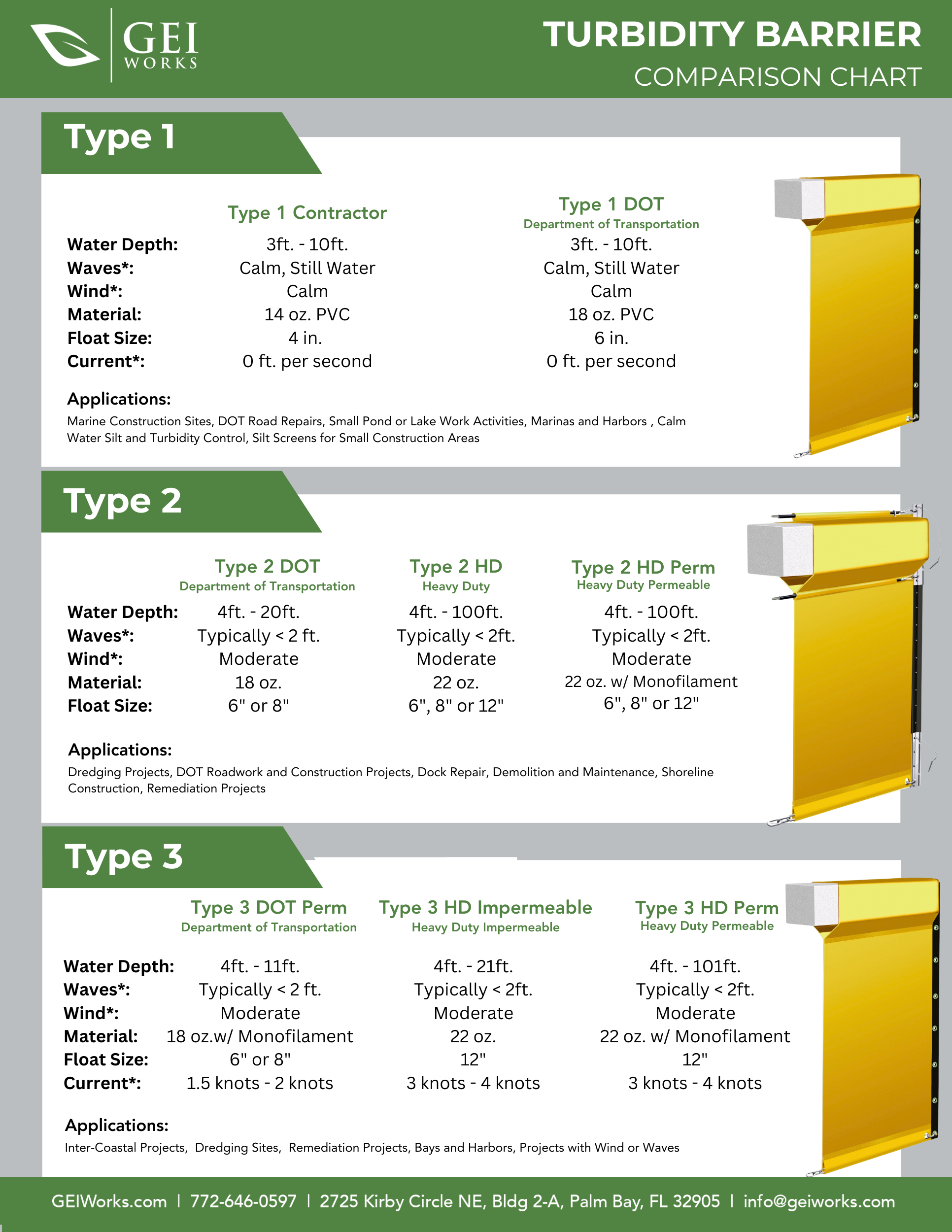
Types of Turbidity Curtains
Depending on project requirements and water conditions, there are three main types of turbidity curtains:
- Type 1 (Calm Water Curtains)
- Designed for use in calm waters with little to no current, such as lakes, ponds, or canals. These are ideal for smaller projects where water conditions are predictable.
- Type 2 (Medium Duty Curtains)
- Suitable for moderate currents, waves, and wind conditions. Commonly used in rivers and harbors, Type 2 curtains offer more durability and stability.
- Type 3 (Heavy Duty Curtains)
- Built for challenging environments with strong currents, tides, or rough weather. These curtains are heavily reinforced and often used in coastal construction or large-scale dredging projects.
Download Turbidity Curtain Comparison Chart
Why Use Turbidity Curtains?
Turbidity curtains play a vital role in environmental protection by:
- Preventing Water Pollution: Contain silt and sediment to prevent water contamination.
They keep sediment and contaminants from spreading to nearby ecosystems.
- Complying with Regulations: Many environmental agencies require sediment control measures to protect water quality during marine construction and construction sites.
- Protecting Marine Life: Reducing sediment spread helps protect aquatic habitats and ensures the health of fish and other wildlife.
Best Practices for Using Turbidity Curtains
To ensure optimal performance, follow these best practices when using turbidity curtains:
- Choose the Right Curtain Type: Match the curtain to the water conditions and project requirements.
- Proper Installation: Make sure the curtain is deployed correctly with no gaps or loose ends.
- Regular Maintenance: Check the curtain for wear and tear, and ensure anchors and floats are secure.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously observe water quality and adjust the curtain as needed to maintain effectiveness.
Turbidity curtains play a crucial role in keeping waterways clean and construction projects compliant. These floating barriers are more than just a helpful tool—they’re a frontline defense against spreading silt and sediment into surrounding waters. When contractors take the time to understand how turbidity barriers work and ensure proper anchoring, they reduce environmental impact while staying within regulatory guidelines. Whether it’s a dredging operation or a marine construction project, the right turbidity curtain keeps sediment in check and progress on track.